Beautiful Soup web scraping tutorial. Contribute to KeithGalli/web-scraping development by creating an account on GitHub. This tutorial was a basic introduction to web scraping with beautiful soup and how you can make sense out of the information extracted from the web by visualizing it using the bokeh plotting library. A good exercise to take a step forward in learning web scraping with beautiful soup is to scrape data from some other websites and see how you can. Create a Beautiful Soup Object and define the parser. Implement your logic. Disclaimer: This article considers that you have gone through the basic concepts of web scraping. The sole purpose of this article is to list and demonstrate examples of web scraping. The examples mentioned have been created only for educational purposes. But we can automate the above examples in Python with Beautiful Soup module. Dos and don’ts of web scraping. Web scraping is legal in one context and illegal in another context. For example, it is legal when the data extracted is composed of directories and telephone listing for personal use. Beautiful Soup Tutorial. In this tutorial, we will show you, how to perform web scraping in Python using Beautiful Soup 4 for getting data out of HTML, XML and other markup languages. In this we will try to scrap webpage from various different websites (including IMDB). We will cover beautiful soup 4, python basic tools for efficiently.
Introduction
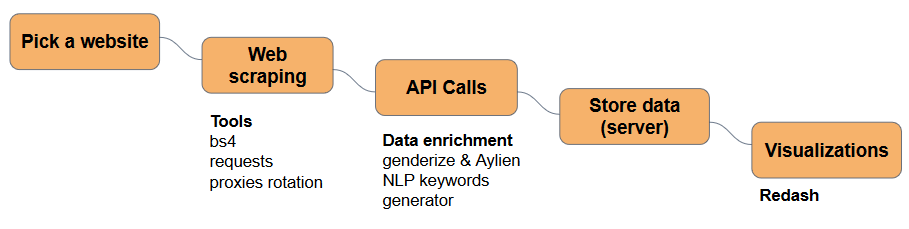
In this tutorial, we will explore numerous examples of using the BeautifulSoup library in Python. For a better understanding let us follow a few guidelines/steps that will help us to simplify things and produce an efficient code. Please have a look at the framework/steps that we are going to follow in all the examples mentioned below:
- Inspect the HTML and CSS code behind the website/webpage.
- Import the necessary libraries.
- Create a User Agent (Optional).
- Send
get()request and fetch the webpage contents. - Check the Status Code after receiving the response.
- Create a Beautiful Soup Object and define the parser.
- Implement your logic.
❖Disclaimer: This article considers that you have gone through the basic concepts of web scraping. The sole purpose of this article is to list and demonstrate examples of web scraping. The examples mentioned have been created only for educational purposes. In case you want to learn the basic concepts before diving into the examples, please follow the tutorial at this link.
Without further delay let us dive into the examples. Let the games begin!
Example 1: Scraping An Example Webpage
Let’s begin with a simple example where we are going to extract data from a given table in a webpage. The webpage from which we are going to extract the data has been mentioned below:
The code to scrape the data from the table in the above webpage has been given below.
Output:
✨ VideoWalkthrough of The Above Code:
Example 2: Scraping Data From The Finxter Leaderboard
This example shows how we can easily scrape data from the Finxter dashboard which lists the elos/points. The image given below depicts the data that we are going to extract from https://app.finxter.com.
The code to scrape the data from the table in the above webpage has been given below.
Output: Please download the file given below to view the extracted data as a result of executing the above code.
✨ Video Walkthrough Of Above Code:
Example 3: Scraping The Free Python Job Board
Data scraping can prove to be extremely handy while automating searches on Job websites. The example given below is a complete walkthrough of how you can scrape data from job websites. The image given below depicts the website whose data we shall be scraping.
In the code given below, we will try and extract the job title, location, and company name for each job that has been listed. Please feel free to run the code on your system and visualize the output.
Output:
✨ Video Walkthrough Of Above Code:
Example 4: Scraping Data From An Online Book Store
Web scraping has a large scale usage when it comes to extracting information about products from shopping websites. In this example, we shall see how we can extract data about books/products from alibris.com.

The image given below depicts the webpage from which we are going to scrape data.
The code given below demonstrates how to extract:
- The name of each Book,
- The name of the Author,
- The price of each book.

Output: Please download the file given below to view the extracted data as a result of executing the above code.
✨ Video Walkthrough Of Above Code:
Example 5: Scraping Using Relative Links
Until now we have seen examples where we scraped data directly from a webpage. Now, we will find out how we can extract data from websites that have hyperlinks. In this example, we shall extract data from https://codingbat.com/. Let us try and extract all the questions listed under the Python category in codingbat.com.
The demonstartion given below depicts a sample data that we are going to extract from the website.
Solution:
Output: Please download the file given below to view the extracted data as a result of executing the above code.
Conclusion
I hope you enjoyed the examples discussed in the article. Please subscribe and stay tuned for more articles and video contents in the future!
Where to Go From Here?
Enough theory, let’s get some practice!
To become successful in coding, you need to get out there and solve real problems for real people. That’s how you can become a six-figure earner easily. And that’s how you polish the skills you really need in practice. After all, what’s the use of learning theory that nobody ever needs?
Practice projects is how you sharpen your saw in coding!
Do you want to become a code master by focusing on practical code projects that actually earn you money and solve problems for people?
Then become a Python freelance developer! It’s the best way of approaching the task of improving your Python skills—even if you are a complete beginner.
Join my free webinar “How to Build Your High-Income Skill Python” and watch how I grew my coding business online and how you can, too—from the comfort of your own home.
I am a professional Python Blogger and Content creator. I have published numerous articles and created courses over a period of time. Presently I am working as a full-time freelancer and I have experience in domains like Python, AWS, DevOps, and Networking.
You can contact me @:
Related Posts
Python offers a lot of powerful and easy to use tools for scraping websites. One of Python's useful modules to scrape websites is known as Beautiful Soup.
In this example we'll provide you with a Beautiful Soup example, known as a 'web scraper'. This will get data from a Yahoo Finance page about stock options. It's alright if you don't know anything about stock options, the most important thing is that the website has a table of information you can see below that we'd like to use in our program. Below is a listing for Apple Computer stock options.
First we need to get the HTML source for the page. Beautiful Soup won't download the content for us, we can do that with Python's urllib module, one of the libraries that comes standard with Python.
Fetching the Yahoo Finance Page
2 4 | optionsUrl='http://finance.yahoo.com/q/op?s=AAPL+Options' |
2 4 | optionsUrl='http://finance.yahoo.com/q/op?s=AAPL+Options' |
This code retrieves the Yahoo Finance HTML and returns a file-like object.
If you go to the page we opened with Python and use your browser's 'get source' command you'll see that it's a large, complicated HTML file. It will be Python's job to simplify and extract the useful data using the BeautifulSoup module. BeautifulSoup is an external module so you'll have to install it. If you haven't installed BeautifulSoup already, you can get it here.
Beautiful Soup Example: Loading a Page
The following code will load the page into BeautifulSoup:
2 | soup=BeautifulSoup(optionsPage) |
Beautiful Soup Example: Searching
Now we can start trying to extract information from the page source (HTML). We can see that the options have pretty unique looking names in the 'symbol' column something like AAPL130328C00350000. The symbols might be slightly different by the time you read this but we can solve the problem by using BeautifulSoup to search the document for this unique string.
Let's search the soup variable for this particular option (you may have to substitute a different symbol, just get one from the webpage):
Beautiful Soup Web Scraping Example Free
2 | [u'AAPL130328C00350000'] |
This result isn’t very useful yet. It’s just a unicode string (that's what the 'u' means) of what we searched for. However BeautifulSoup returns things in a tree format so we can find the context in which this text occurs by asking for it's parent node like so:
2 | >>>soup.findAll(text='AAPL130328C00350000')[0].parent <ahref='/q?s=AAPL130328C00350000'>AAPL130328C00350000</a> |
We don't see all the information from the table. Let's try the next level higher.
2 | >>>soup.findAll(text='AAPL130328C00350000')[0].parent.parent <td><ahref='/q?s=AAPL130328C00350000'>AAPL130328C00350000</a></td> |
And again.
2 | >>>soup.findAll(text='AAPL130328C00350000')[0].parent.parent.parent <tr><td nowrap='nowrap'><ahref='/q/op?s=AAPL&amp;k=110.000000'><strong>110.00</strong></a></td><td><ahref='/q?s=AAPL130328C00350000'>AAPL130328C00350000</a></td><td align='right'><b>1.25</b></td><td align='right'><span id='yfs_c63_AAPL130328C00350000'><bstyle='color:#000000;'>0.00</b></span></td><td align='right'>0.90</td><td align='right'>1.05</td><td align='right'>10</td><td align='right'>10</td></tr> |
Bingo. It's still a little messy, but you can see all of the data that we need is there. If you ignore all the stuff in brackets, you can see that this is just the data from one row.
2 4 | [x.text forxiny.parent.contents] foryinsoup.findAll('td',attrs={'class':'yfnc_h','nowrap':'}) |
This code is a little dense, so let's take it apart piece by piece. The code is a list comprehension within a list comprehension. Let's look at the inner one first:
foryinsoup.findAll('td',attrs={'class':'yfnc_h','nowrap':'}) |
This uses BeautifulSoup's findAll function to get all of the HTML elements with a td tag, a class of yfnc_h and a nowrap of nowrap. We chose this because it's a unique element in every table entry.
If we had just gotten td's with the class yfnc_h we would have gotten seven elements per table entry. Another thing to note is that we have to wrap the attributes in a dictionary because class is one of Python's reserved words. From the table above it would return this:
<td nowrap='nowrap'><a href='/q/op?s=AAPL&amp;k=110.000000'><strong>110.00</strong></a></td> |
Beautiful Soup Web Scraping Examples
We need to get one level higher and then get the text from all of the child nodes of this node's parent. That's what this code does:
Beautiful Soup Web Scraping Example Pdf
This works, but you should be careful if this is code you plan to frequently reuse. If Yahoo changed the way they format their HTML, this could stop working. If you plan to use code like this in an automated way it would be best to wrap it in a try/catch block and validate the output.
Beautiful Soup Web Scraping Tutorial
This is only a simple Beautiful Soup example, and gives you an idea of what you can do with HTML and XML parsing in Python. You can find the Beautiful Soup documentation here. You'll find a lot more tools for searching and validating HTML documents.
